
Every internet workspace is empty without an open-source web server software. When websites struggle with slow load times, server crashes, and heavy traffic, the Nginx server might be the answer.
Known worldwide for handling millions of connections with ease, Nginx is used for building the foundation of some of the busiest websites on the internet. Pronounced as ‘engine-ex’, it is an open-source web server. It was first released in October 2024, and over the past 20 years, the server has evolved above and beyond.
From Microsoft, IBM, to Google, LinkedIn, Apple, and Intel, the leading industry names rely on Nginx for their server needs. Join us to learn more about what is Nginx, what is Nginx used for, and other similar questions.
What is Nginx?
Nginx, or engine-x, is an open-source web server software – a definition that you will read everywhere.
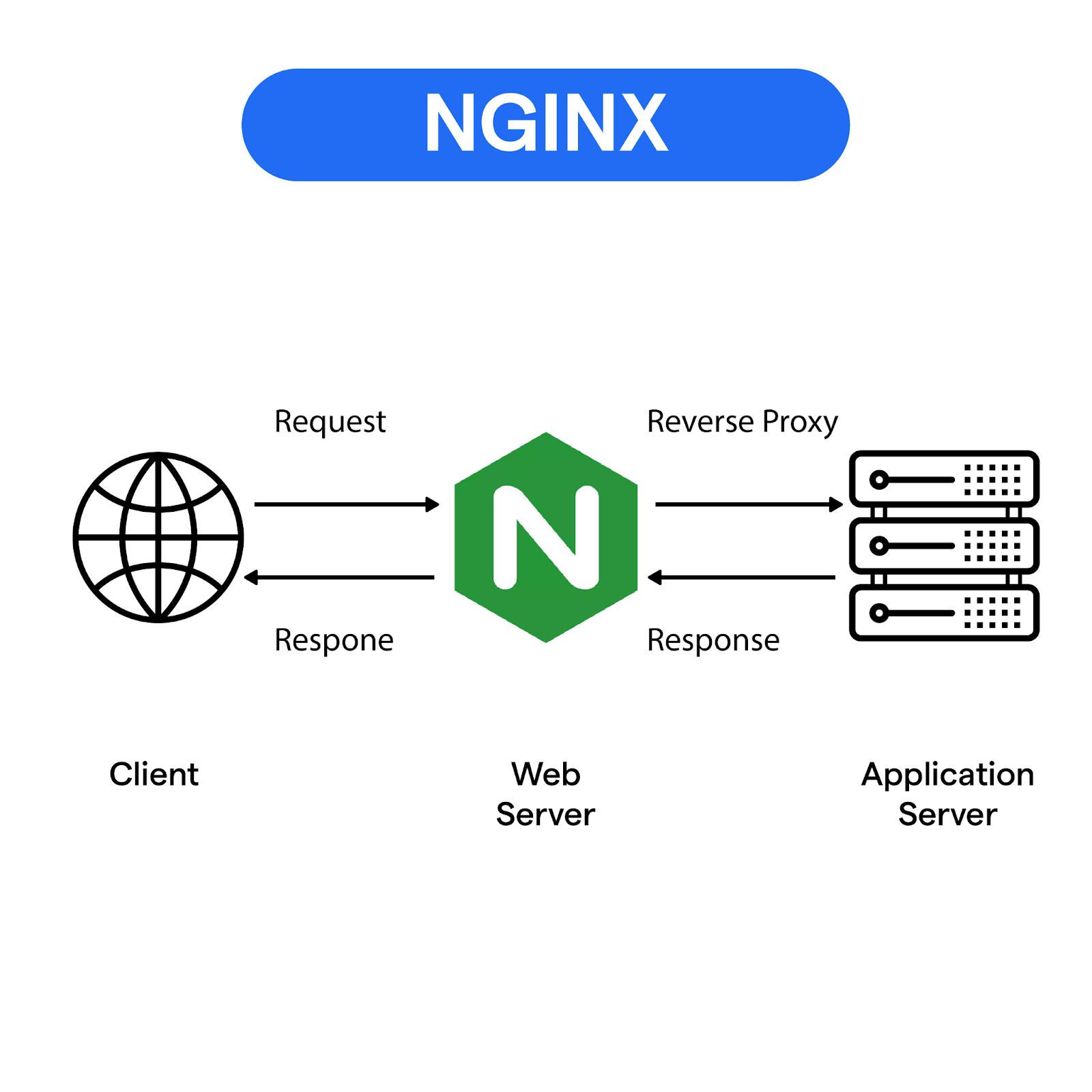
But it isn’t just another web server. Nginx is a business enabler with event-driven architecture that can act as a reverse proxy, load balancer, and even a caching layer. This versatile tool in the modern infrastructure handles traffic, balances load, and content at lightning speed for some of the busiest websites in the online world. It gives you control over routing, security, and scalability, but still keeps away from overcomplicating your stack. In simpler words, you can understand Nginx as the traffic manager for the internet that guides every request to the right direction.
Nginx is a brainchild of Igor Sysoev that came around in late 2004. Sysoev aimed to solve the C10K problem (handling 10,000+ connections at once) and did it successfully. The server was created for Russian web portals, but its effectiveness led to worldwide adoption. Straight away, after over 20 years, F5 Networks and a large open-source community support Nginx today.
Think of the moment you click a link online. Behind that instant response is software like Nginx, making sure pages load without delay and traffic is handled smoothly.
Why is Nginx called “engine-x”?
Nginx is read as engine-x. The name was coined by Igor Sysoev back in 2004, when he was trying to solve the problem of handling thousands of web connections at once.
- “Engine” stands for the strong core running the web.
- “X” suggests multiplexing, or simply a cool tech twist.
Put together, it became a short and memorable name that pointed to speed and efficiency.
DEMO IMAGE
What makes Nginx different from Apache?
When choosing between Apache and Nginx, it helps to see where they differ:
1. Architecture
Apache → thread or process per request.
Nginx → event-driven, asynchronous handling.
2. Performance
Apache → good with PHP and dynamic content.
Nginx → great with static files, very efficient with resources.
3. Configuration
Apache → .htaccess allows directory-level tweaks.
Nginx → central config, faster but less flexible.
4. Resources
Apache → heavier under high load.
Nginx → lean and stable with concurrent traffic.
5. Reverse proxy
Apache → needs modules.
Nginx → built-in support.
While Apache shines for its versatility and long track record, Nginx stands out for being lightweight and built for growth.
What is Nginx used for?
If you’re wondering what is Nginx used for, the short answer is: a lot more than you think. It’s not just a web server; it’s a toolkit for handling modern internet traffic.
Here are some of the ways Nginx is used:
- Nginx, at its core, is a web server software. It delivers static content like HTML, CSS, images, and video fast and efficiently.
- As a reverse proxy, it shields backend servers and manages requests smartly.
- As a load balancer, it shares traffic across servers so apps don’t go down under pressure.
- It is also a mail proxy that supports IMAP, POP3, and SMTP in big organisations.
As an API gateway, Nginx is used in microservice architectures where requests need to be routed, filtered, or rate-limited.
How Does Nginx Work?
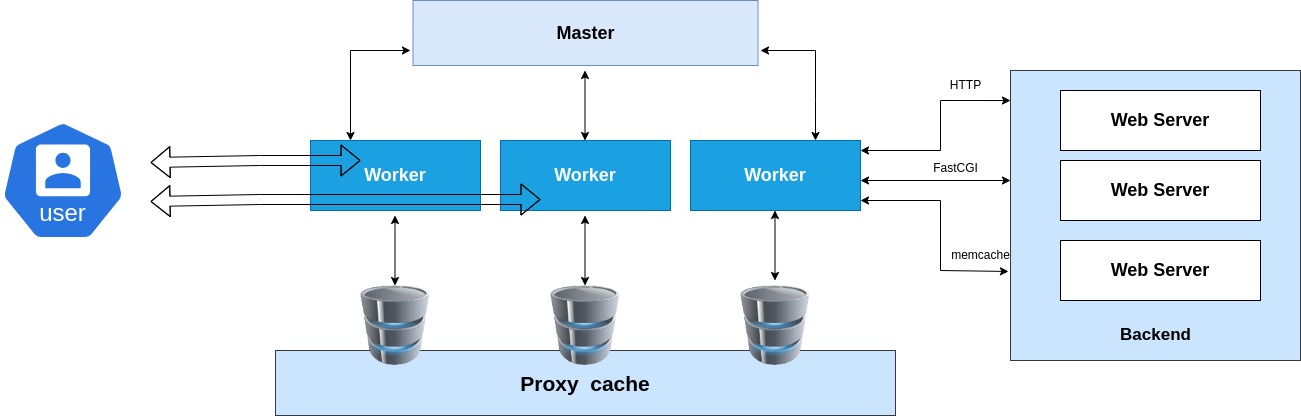
- Event-driven, asynchronous architecture – Nginx, as mentioned right above, uses an asynchronous architecture, or you can say a master-slave architecture. In this model, the master process assigns tasks based on client requests to the worker processes.
- The Master-worker process model – Once the master assigns tasks to the worker, the master doesn’t wait for the worker’s response but immediately proceeds to handle the next client request.
Later, as the worker completes tasks and sends back the response, the master will forward it to the client.
- Handling concurrent operations – This flow of design allows Nginx to manage multiple client requests concurrently and efficiently without a delay.
In the Nginx architecture, workers are processes subordinate to the master. Every worker can handle over 1000 requests simultaneously in a single-threaded fashion. It saves on RAM and storage by running everything in the same memory space – rather than spreading work across separate ones like multi-threaded processes do.NGINX reduces delays by pulling pages from cache memory. The system saves the page when first accessed and reuses it later for faster performance.
Key Features of Nginx
- It delivers static files (images, videos, and stylesheets) instantly without straining the system hardware.
- It balances traffic between multiple servers, making sure no single one is overworked.
- It terminates SSL/TLS and keeps the connections safe.
- It will boost your site’s speed through caching and by supporting HTTP/2.
So, what makes Nginx stand out?
Nginx is a lightweight and event-driven model that can perform excellently even under pressure. It is robust, quick, and scalable and thus a go-to for websites that can’t afford downtime.
A Look into Nginx’s Popularity
Millions of websites you access daily on the internet, including Twitter, Netflix, and Airbnb, swear by Nginx. This server has made itself a place where developers working on cloud-native and container-based setups trust it.
Advantages of Nginx
- Performance: Nginx is built to be fast and performant. Its architecture keeps a single thread for each visitor, saving memory and processor power. Since the server handles requests without blocking, it keeps responses fast and traffic steady. That’s why sites delivering static files—like images, CSS, and JS—prefer using it.
- Scalability: Another big advantage is scalability. Nginx adapts easily as your site grows. A website that starts small can scale to millions of visitors without switching platforms. Since it handles load balancing and reverse proxying by default, it directs traffic to multiple servers, avoiding stress on just one.
- Reliability: Reliability matters for any online system, and Nginx scores here, too. It can run for long periods without crashing. Companies rely on it since downtime can be costly. Nginx’s built-in tools make sure another server steps in immediately if one goes down.
- Cost-effective: The cost advantage is real as well. Nginx is free to use under open source, and the paid version, Nginx Plus, is optional. Since it requires fewer resources, you save money on hardware. Even small companies benefit because they don’t have to invest in powerful, costly machines.
Disadvantages of Nginx
On the other side, there are limits.
- Complex configuration: Apache users often miss .htaccess support. In Nginx, you make all changes in one central configuration file, which feels restrictive in shared hosting.
- Learning Curve: Beginners may also struggle with its configuration. The syntax is different from Apache, and advanced setups need proper learning. The module ecosystem is also smaller. If you are having difficulty with the configuration setup, you can always contact the FlexiCloud technical team and we will do the rest of the work for free.
- Limited Built-in modules: Apache comes with many plug-ins, but Nginx depends on outside tools for some tasks. For most websites, its speed and performance are worth the trade-off.
Nginx Vs. Apache
Apache is like the old guard of web servers. It has a long history and a huge global community. Because of this, plenty of documentation, plug‑ins, and support are always available. Apache is often seen as the “easy entry point,” especially for beginners or developers working on small to medium sites. It supports dynamic configurations through .htaccess, which many shared hosting companies rely on.
Nginx is a modern player focused on today’s internet needs. Instead of heavy processes, it uses events to manage requests efficiently. It makes static items like CSS, videos, and images available quickly. At the same time, it manages SSL, caching, and traffic distribution on its own, which matches the needs of microservice and container platforms.
Apache works well when a project needs deep customisation or older scripting support. But Nginx excels in raw speed, easy scaling, and stability under heavy traffic.
The choice isn’t about one being better, but which fits the project’s needs. Small blogs may find Apache comfortable, while huge traffic sites often can’t do without Nginx.
How to Install Nginx in Ubuntu?
If you have stuck till here knowing what is Nginx server, have a look at how you can install it on Ubuntu –
Step 1: Install Nginx
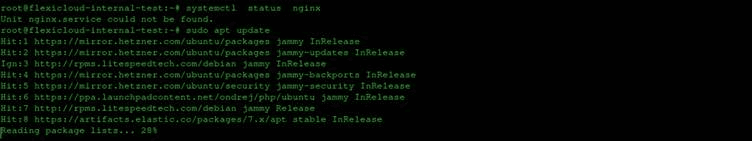
Open a terminal and update the repository using the following command:
# sudo apt update
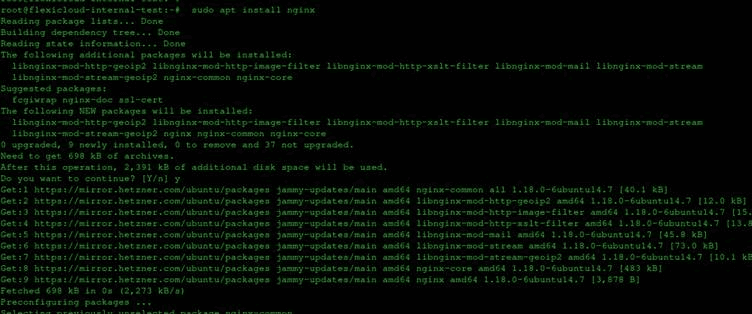
Now, run:
# sudo apt install Nginx
And install Nginx
S
Step 2: Firewall Adjustment
You can’t test Nginx without adjusting the firewall software, or you won’t be able to access the service. Once done, Nginx will register itself with ufw, giving simple access.
Now, to get a list of application settings (familiar with ufw), run the following command:
# sudo ufw app list
You have three Nginx profiles to pick from:
· Nginx Full: Opens both 80 and 443.
· Nginx HTTP: Opens just port 80 (normal traffic).
· Nginx HTTPS: Opens just port 443 (secure traffic).
Always allow only what’s needed. For now, limit it to port 80.
To enable it, run the command:
# sudo ufw allow ‘Nginx HTTP’
To verify the change, run the command:
# sudo ufw status
With the output, you will be able to see which HTTP traffic is allowed.
Step 3: Check the Web Server
You hit ‘install complete,’ Ubuntu kicks Nginx up straight away. No asking, no warning — server’s just there, active.
To know if the service is running using systemd init, run the command:
# systemctl status Nginx
In case Nginx is inactive or failing to run, you must run the Nginx service with the command:
# systemctl start Nginx
Now re-enable the service with the command below:
# systemctl enable Nginx
Visit the browser address bar and enter your server’s IP address:
http://<your_server_ip>
If your installation was successful, it will display as below:
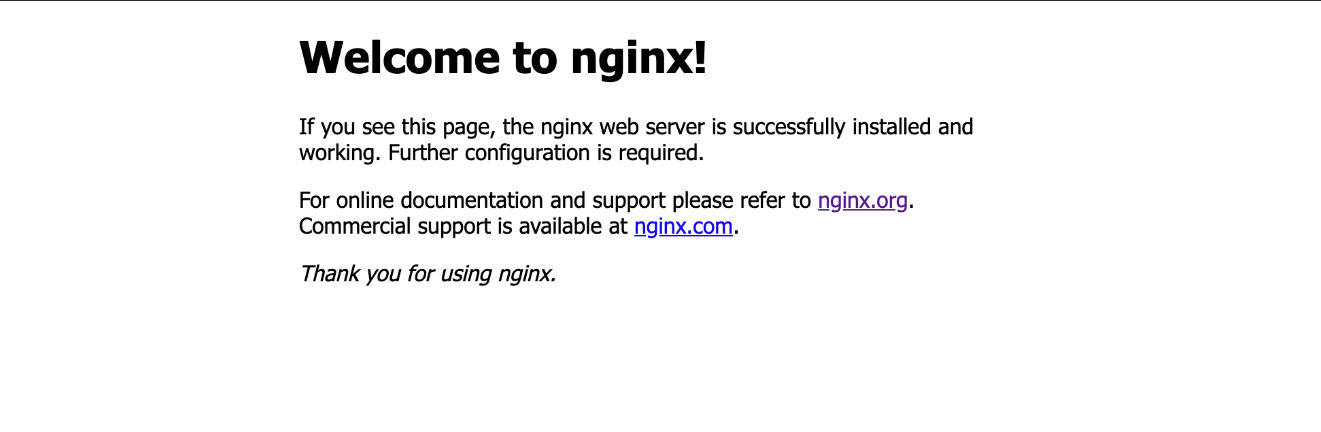
All we’ve done here is install Nginx. To host a website, you’ll still need to edit its configuration files.
Conclusion
By now, you’ll see why Nginx is more than just a web server. It’s fast with static files, smart with traffic, and reliable enough for some of the busiest websites you use every day. The way it works — with its master and worker setup, non-blocking design, and built-in tools — makes it different from Apache and a natural fit for today’s internet. If you’re setting up a project that requires speed and scale, FlexiCloud’s VPS plans provide an optimized Linux environment suitable for running NGINX. FlexiCloud’s expert technical team will help you configure NGINX, install the necessary modules, and adjust settings to meet your requirements.
FAQs
1. What is an Nginx server?
Nginx is a free web server software that helps deliver websites fast by handling many visitors at once.
2. Is Nginx better than Apache?
Both are good, but Nginx is preferred today for fast websites and handling heavy web traffic smoothly.
3. Is Nginx free?
Nginx’s free version already supports the most needed features for web hosting and proxying.
4.Can I use Nginx with WordPress?
You may need some setup for caching and permalinks, but Nginx supports WordPress fully.